This behavior is due to the automatic Metric feature on windows.
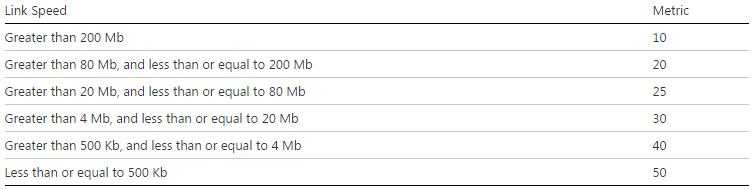
As you can see on the table below if I am connected on a 100Mb, my metric on the copper is 20.
On our site, we have 802.11a/g and 802.11a/g/n access points.
- When I'm on an a/g antenna (max 54Mbps) and a 100Mb copper inteface, I have the following routing table:
C:\Users\ABCD>netstat -rn
IPv4 Route Table
========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.254 10.1.1.32 20
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.2.254 10.1.2.68 25
- When I'm on a a/g/n antenna (and my bandwith is more than 200Mb) and a 100Mb copper inteface, I have the following routing table:
C:\Users\ABCD>netstat -rn
IPv4 Route Table
========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.2.254 10.1.2.68 10
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.254 10.1.1.32 20
As you can see the wireless is preferred with a metric of 10. I have chosen the solution to fix by myself the metric on networks interfaces (copper 1 and wireless 20).
start>control Panel>Network and Sharing Center>Change adpater settings
Right click on the Copper card>Properties>Internet Protocol Version 4>Properties>Advanced
Uncheck 'Automatic metric' and fix the metric
For my case, I'm only using the interface metric. But the result in metric seen with the command 'netstat -rn' is the result of an addition (Gateway metric + InterfaceMetric).
In order to find the gateway metric, you can use the command 'netsh int ip show config':
C:\Users\ABCD>netsh int ip show config
Configuration for interface "Local Area Connection"
DHCP enabled: Yes
IP Address: 10.1.1.32
Subnet Prefix: 10.1.1.0/24 (mask 255.255.255.0)
Default Gateway: 10.1.1.254
Gateway Metric: 0
InterfaceMetric: 20
DNS servers configured through DHCP: 10.1.2.5
Register with which suffix: Primary only
WINS servers configured through DHCP: None
Configuration for interface "Wireless Network Connection"
DHCP enabled: Yes
IP Address: 10.1.2.68
Subnet Prefix: 10.1.2.0/25 (mask 255.255.255.0)
Default Gateway: 10.1.2.254
Gateway Metric: 0
InterfaceMetric: 25
DNS servers configured through DHCP: 10.1.2.5
Register with which suffix: Primary only
WINS servers configured through DHCP: None



